There’s a pretty decent chance you’ve heard of a little company called Uber. It was a Crunchies finalist back in 2011 (for Best Location Application, alongside Runkeeper, Foursquare, Airbnb and Grindr), and it’s been doing rather well ever since.
As I am writing this, Uber has a $69 billion market cap (nice) and it’s a global superstar startup.
But it wasn’t always like this. Fifteen years ago, the company set out to raise a $200,000 round of financing with a different name (UberCab) and a different business model (limos you hail from your smartphone using SMS). In 2011, it launched in San Francisco, followed quickly after that in a number of other cities.
A lot has changed in the past 15 years. For one thing, the original iPhone had only just been launched (without the ability to install apps!), and fundraising has become a lot more sophisticated.
The Uber deck has been floating around the internet for a while; we shared it as a gallery back in 2017, and these days it isn’t really seen as a good example of how to do a pitch deck. Even still, let’s take a stroll down memory lane and see what Uber got right in its original pitch — and where it made some spectacularly silly mistakes.
We’re looking for more unique pitch decks to tear down, so if you want to submit your own, here’s how you can do that.
Slides in this deck
- Cover slide
- Problem slide (“Cabs in 2008”)
- Solution slide (“Digital Hail can now make street hail unneccessary”)
- Solution slide (“UberCab Concept”)
- Product slide 1 (“1-Click Car Service”)
- Value proposition slide 1 (“Key Differentiators”)
- Mission (“Operating Principles”)
- How it works slide 1 (“UberCab Apps”)
- How it works slide 2 (“UberCab.com”)
- Positioning slide (“Use Cases”)
- Value proposition slide 2 (“User Benefits”)
- Value proposition slide 3 (“Environmental Benefits”)
- Product slide 2 (“UberCab Fleet”)
- Go-to market slide 1 (“Initial Service Area”)
- Technology overview slide (“Technology”)
- Competitive advantage slide (“Demand Forecasting”)
- Market size slide (“Overall Market”)
- Market segmentation slide (“Composition of Market”)
- Go-to-market slide 2 (“Target Cities”)
- Scenario planning (“Potential Outcomes”)
- “Why now?” slide (“SmartPhones Aug 2008”)
- Road map slide 1 (“Future Optimizations”)
- Marketing slide (“Marketing Ideas”)
- Road map slide 2 (“Location-Based Service”)
- Traction slide (“Progress to Date”)
Three things to love
There are some beautiful historical gems in this slide deck, some of which are just delightful idiosyncrasies of a time gone by. Others are legitimately insightful glimpses into where Uber would be growing, visible even in this very early deck.
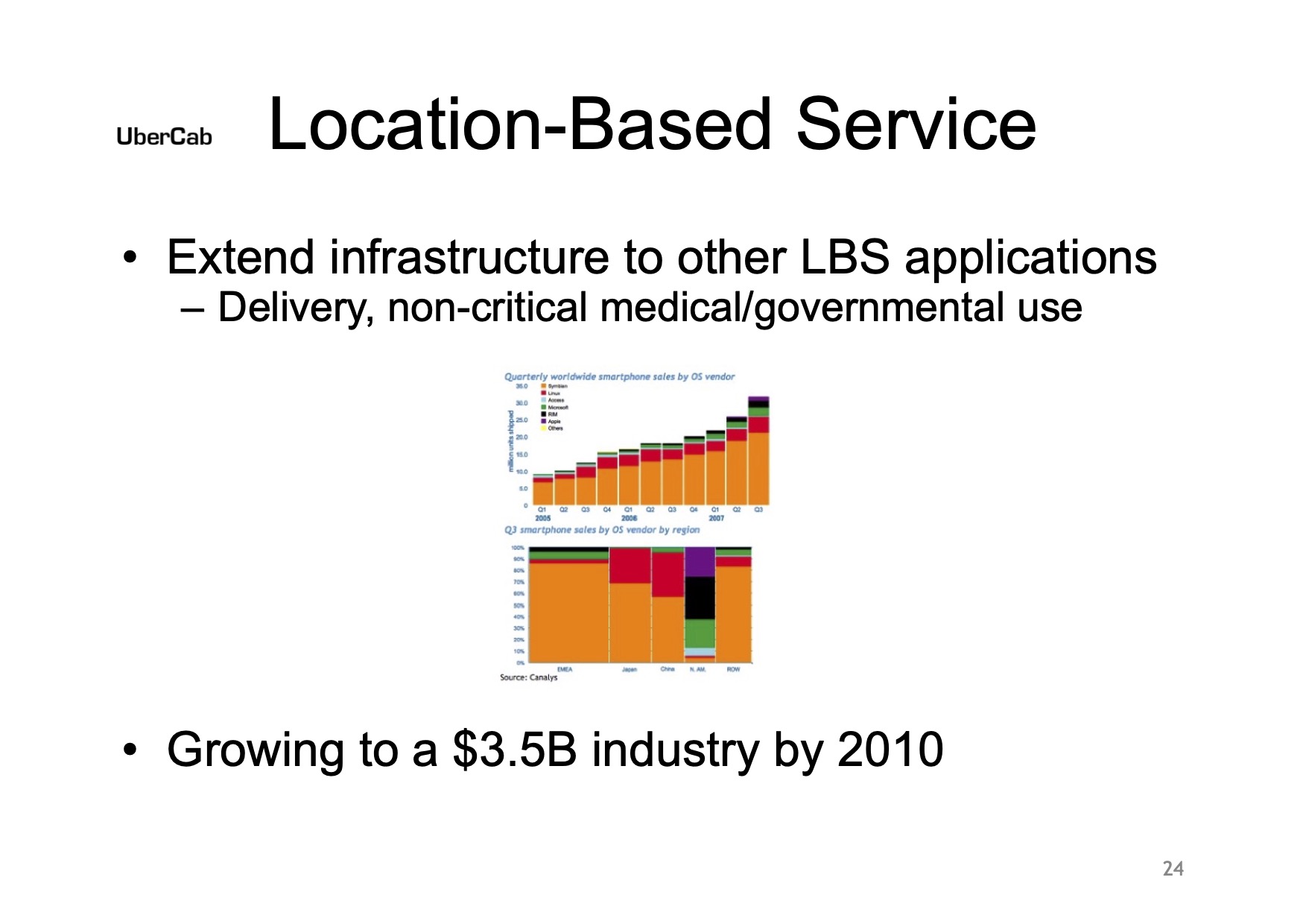
Uber knew location-based services would be huge
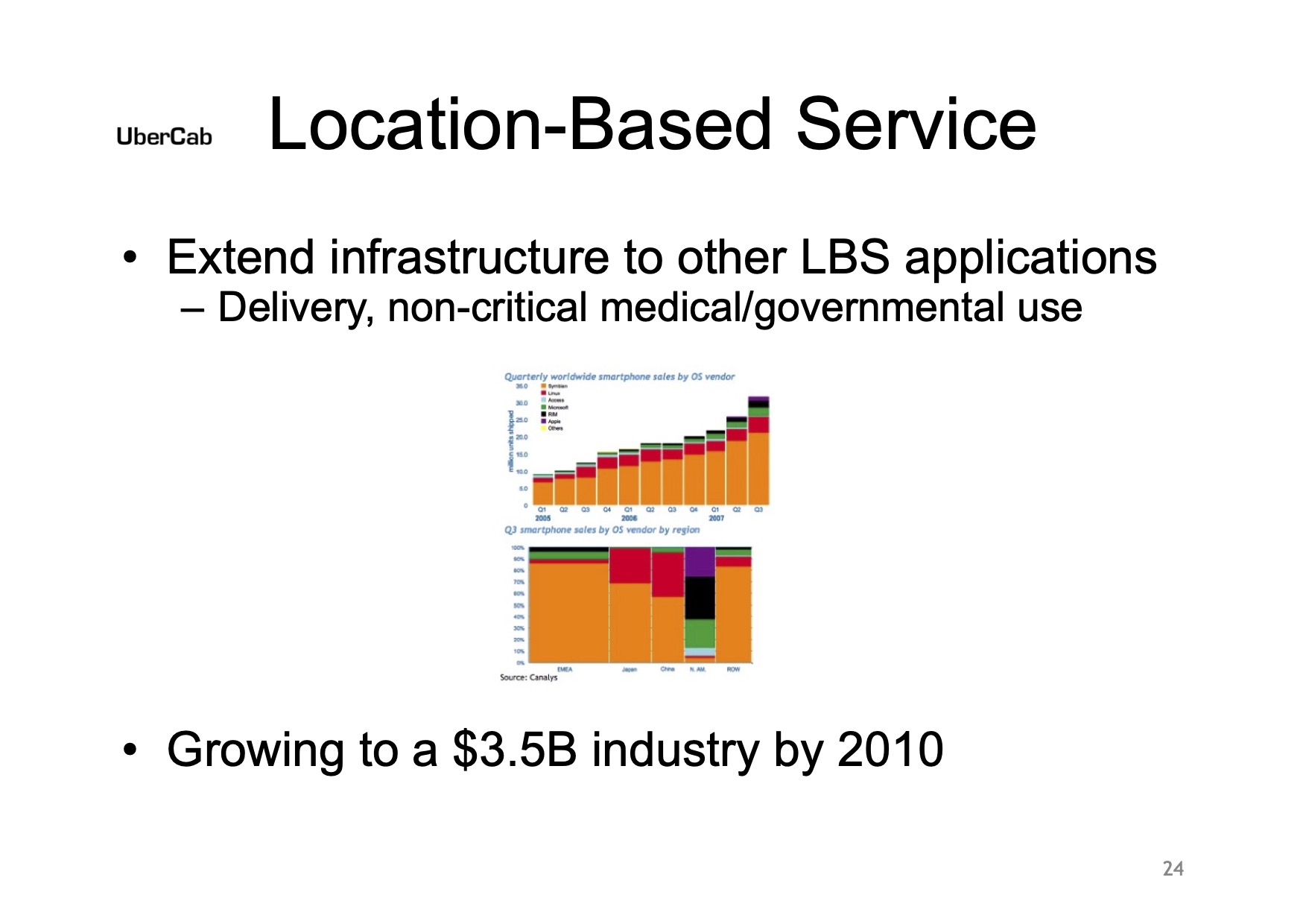
[Slide 24] Uber knew from the start that it might have adjacent markets as an option. Image Credits: Uber
Today, it’s hard to imagine a world without Uber in it, but even in this slide deck, it’s clear that Uber likely didn’t know how big of an impact it would have, but it knew it was in the space of “location-based services.”
The Lyft-pioneered hailing-a-ride-from-a-random-stranger model came later, but Uber knew that delivery was going to be a key source of growth. The company projected that this would be a $3.5 billion industry by 2010. Considering that Uber Eats raked in around $8 billion in 2021 and nearly $11 billion last year, it’s pretty safe to say Uber’s projections turned out to be right.
That was a particularly fascinating thought back in 2008 because Uber had yet to launch and didn’t have a clear vision for how it was going to launch UberX.
Made possible by smartphones
Of course, with the benefit of hindsight, this is a fantastically obvious one, but …
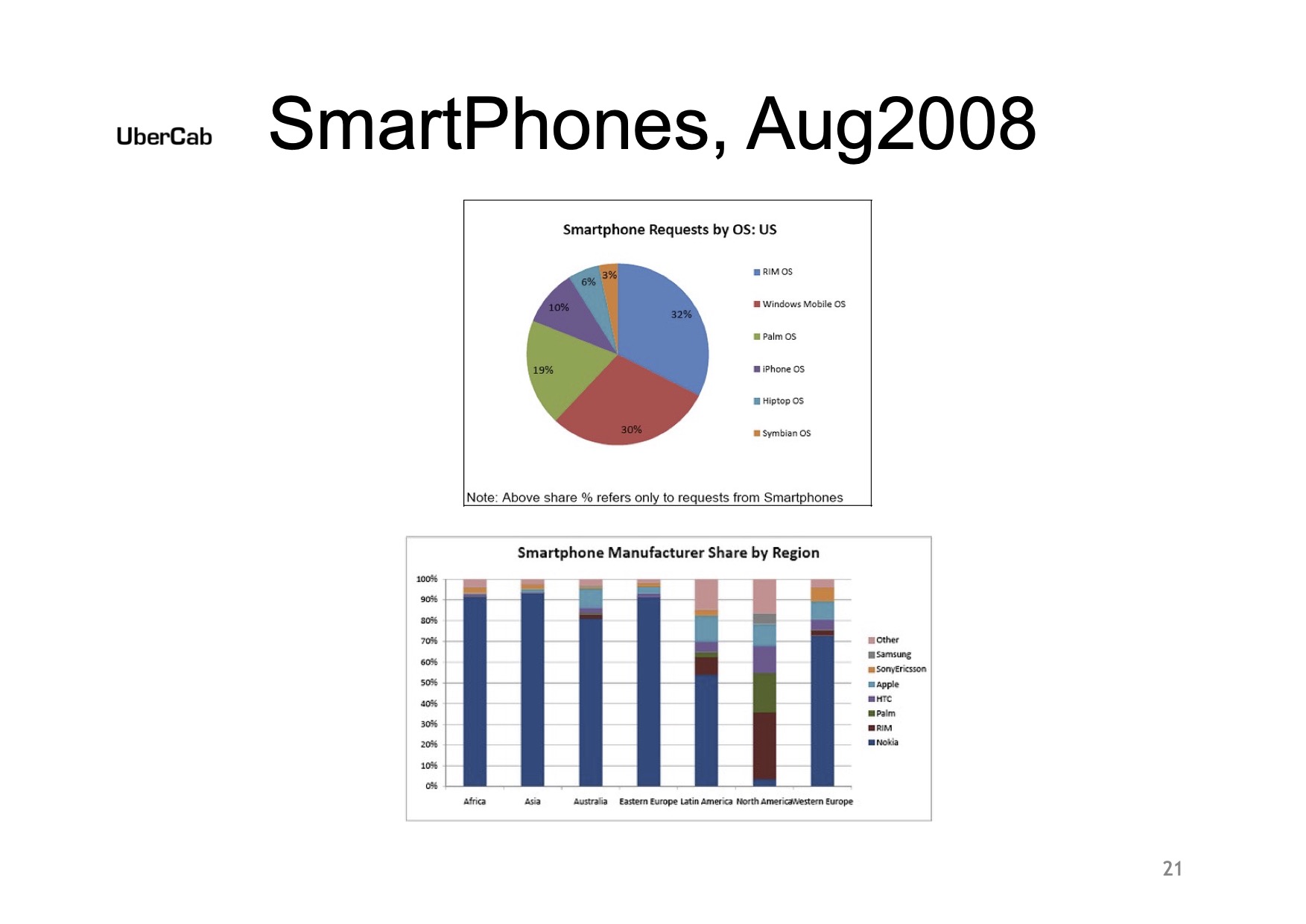
[Slide 21] SmartPhones. They’re a thing. Image Credits: Uber
In 2008, smartphones were starting to be a thing. According to Uber’s deck, BlackBerry led the pack with a 32% market share, followed by Windows Mobile (30%), Palm OS (19%), iPhone (10%), Hiptop (6%) and Symbian (3%). It’s pretty wild to consider that out of all of those operating systems, these days, most of those don’t even exist. Apple’s iOS sits at a 60%-ish market share in the U.S., with Android holding the rest. And then there are some also-rans.
The interesting — and crucial — thing was that the smartphone (and ubiquitous data availability on cellphone plans) was ultimately the technology that unlocked Uber’s current business model: Drivers can drive, passengers can hail, etc. The company doesn’t make much of a prediction of where the market is going, but it knew one thing: SmartPhones [sic] were an important part of the path going forward.
As a startup, Uber is showing that it is, in effect, building a company on two emerging technologies: location-based technologies and smartphones. That’s pretty genius, everything considered. And there’s an important thing that can be learned from this when you’re building your own pitch deck: Tying your company to major macroeconomic or technology shifts is a great way to catch a tremendous tailwind.
What’s the (best/worst) that could happen?

[Slide 20] OK, this is just funny. Image Credits: Uber
As a founder, you really shouldn’t have an “exit” slide on your pitch deck. It’s unknowable and silly. I am including it here because of how wonderfully, painfully wrong it is.
Uber’s founders, in their wildest dreams, imagined that the best-case scenario was $1 billion in annual revenue. To be fair, the $8.6 billion it generated in 2022 is more than $1 billion, so the company was, indeed, right. But it also hoped for a “realistic” scenario of $20 million to $30 million per year of profit. That’s an interesting one — because for ever-so-many years, Uber was running at a significant loss as it was optimizing for aggressive growth over profits. I love this slide so much.
The lesson here? Get rid of any sort of predictions about your exits or outcomes. Size the market and call it a day.
In the rest of this teardown, we’ll take a look at three things Uber could have improved or done differently.